The difference between MIM and powder metallurgy?
MIM (Metal Injection Molding) and traditional Powder Metallurgy (PM) are both manufacturing techniques that use
metal powder to produce metal parts, but they differ in terms of the manufacturing process and applicable product
characteristics.
Powder Metallurgy technology:
Powder metallurgy refers to the process of producing metal parts by pressing metal powder or a mixture of non-metal
powder and sintering at high temperature. In this process, the powder is pressed into a cold mold to form the desired
shape, and then the powder particles are diffused and bonded by heat treatment in a sintering furnace.
The characteristics of powder metallurgy are as follows:
Suitable for the production of simple shape, relatively large size and mass production parts.
Since there is no melting process, powder metallurgy can avoid oxidation and other problems associated with melting.
The material utilization rate is high and can basically reach the near-net formation type.
Materials that can produce a certain porosity are suitable for special applications such as filtration and bearing.
Some properties (such as strength) may be lower than full-density products of the same material.
MIM Metal Injection Molding:
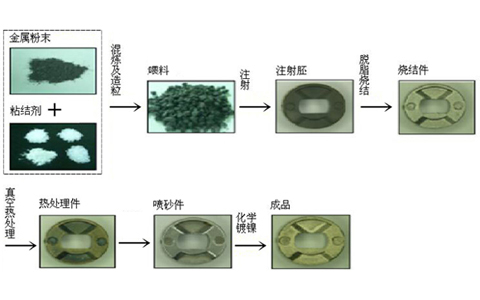
MIM technology combines the features of powder metallurgy and plastic injection molding. First, the metal powder
and polymer binder are thoroughly mixed to make a uniform feed, and then an injection molding machine is used
to inject it into the mold to form the desired shape. Next, the binder is removed by a chemical or thermal degreasing
process, and finally the parts are densified by high-temperature sintering.

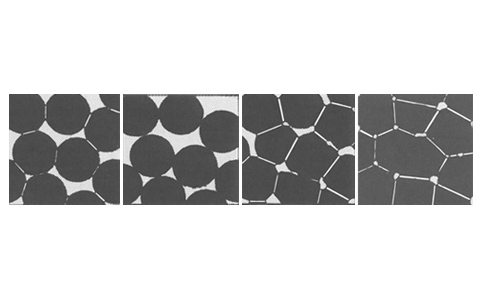
MIM features are as follows:
It can produce metal parts with complex shape, high precision and small size.
Suitable for mass production of small precision components, especially those
that are difficult or impossible to produce cost-effectively by traditional methods.
High material utilization, near net formation, reducing subsequent processing costs.
Usually requires a high initial investment and is suitable for high volume
production to achieve cost effectiveness.
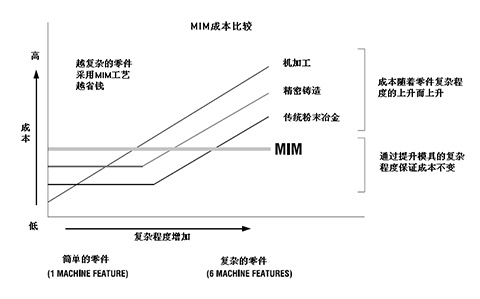
In SUMMARY:
MIM technology is suitable for small, complex precision parts, which can achieve high production efficiency and excellent mechanical properties. Traditional powder metallurgy is more suitable for the production of simple shape, large size and porosity requirements of the parts. Each has its own advantages, and the specific application depends on production needs and target costs.
